The Kstone acrylic solid surface technical specifications
The following sample(s) was/ were submitted and identified on behalf of the client as:
Sample Name : ACRYLIC SOLID SURFACE
Sample No : SC100220106
Test Required : Please see next pages
Test Method : Please see next pages Product specification : 3680 ×760×12MM
Manufacturer : SHANGHAI KSTONE INDUSTRIAL CO.,LTD
Date of Receipt : Feb.05,2018
Test Period : Feb.05,2018 to Mar.31,2018
1.Abrasion resistance, Barcol hardness, Tensile strength, Flexural strength, Density, Water absorption, High temperature resistance, Boiling water resistance, Coefficient of linear thermal expansion
Test Result:
| Test Item | Test Method | Test Condition | Test Result |
|
Abrasion resistance |
ASTM D4060-07 |
Load: 500g/wheel Wheel: CS-10 Total 5000 cycles |
Weight loss: 156.8mg |
| Barcol hardness | ASTM D2583-07 | Thickness: 12.15mm | 33 |
|
Tensile strength |
ASTM D638-08 |
Specimen width: 13.2mm Specimen thickness: 4.0mm Testing speed: 50mm/min |
33.9MPa |
|
Flexural strength |
ASTM D790-07ε1 |
Specimen: 127mm×12.9mm×4.0mm Testing speed: 2mm/min
Span: 64mm |
51.1MPa |
| Density | ASTM D792-08 | —- | 1717.5 kg/m3 |
| Water absorption | ASTM D570- 98(2005) | —- | 0.038% |
| High temperature resistance |
NEMA LD3-2005 |
Specimen: 200mm×200mm Hot wax method 180℃, 20min |
No effect |
| Boiling water resistance | NEMA LD3-2005 | Specimen: 200mm×200mm | No effect |
| Coefficient of linear thermal expansion | With reference to ASTM D696-08 | -30℃~30℃ | 3.2×10-5/℃ |
1.Stain resistance, Chemical resistance, Ball impact resistance
| Test Item | Test Method | Test Result |
| Stain resistance | NEMA LD3-2005 | Total Score:13 See Appendix A |
| Chemical resistance | With reference to
ANSI Z124.1-1995 |
See Appendix B |
| Ball impact resistance | NEMA LD3-2005 | See Appendix C |
| Test Reagent Number | Stain | Grade | Test Result |
| 1 | Distilled water | 0 | No effect |
| 2 | Ethyl alcohol solution | 0 | No effect |
| 3 | Acetone | 6 | Severe effect |
| 4 | Household ammonia | 0 | No effect |
| 5 | 10% Citric acid | 0 | No effect |
| 6 | Vegetable oil | 0 | No effect |
| 7 | Fresh coffee | 0 | No effect |
| 8 | Fresh tea | 0 | No effect |
| 9 | Catsup | 0 | No effect |
| 10 | Yellow mustard | 0 | No effect |
| 11 | 10% Povidone iodine | 3 | Moderate effect |
| 12 | Black permanent marker | 1 | Moderate effect |
| 13 | #2 pencil | 1 | Moderate effect |
| 14 | Wax crayon | 1 | Moderate effect |
| 15 | Black paste shoe polish | 1 | Moderate effect |
| Remark Sample | dimension: 400mm×100mm×12mm, 1pcs | ||
Appendix B: Test result of Chemical resistance:
| Chemicals Number | Chemicals name | Test Result |
| 1 | 10% acetic acid | Not affected |
| 2 | 0.10M nitric acid (HNO3) | Not affected |
| 3 | 0.10M hydrochloric acid (HCl) | Not affected |
| 4 | 0.10% sodium hydroxide | Not affected |
| 5 | Ammonia solution | Not affected |
| 6 | 10% Sodium hypochlorite solution | Affected |
| 7 | 10% sodium hydroxide | Affected |
| 8 | Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) | Not affected |
| 9 | Acetone | Affected |
| 10 | Toluene | Not affected |
| 11 | 1.0M nitric acid | Not affected |
| 12 | 50% sodium hydroxide | Affected |
| 13 | Methyl ethyl ketone | Affected |
| 14 | Glacial acetic acid | Affected |
| 15 | Chloroform (CHCl3) | Affected |
| 16 | Methyl methacrylate | Affected |
| 17 | Aqua regia | Affected |
| 18 | 11M nitric acid (HNO3) | Affected |
| 19 | 10M hydrochloric acid (HCl) | Affected |
| 20 | Methylene chloride (CH2Cl2) | Affected |
| Remark | The chemicals list was offered by client. | |
Appendix C: Test result of ball impact resistance:
| The height of ball | Test result |
| 3.5m | The sample is not broken. |
| Remark | The sample is bonded to particleboard utilizing a PVAc adhesive. |
1.Colorfastness test
Test standard: ANSI Z124.3-2005
Xenon-arc exposure in accordance with ASTM D2565-99(2008) Test Condition: Irradiance: (0.35±0.02)W/(m2·nm)@340nm
Continuous light at (63±5)℃ BPT
Filter: Daylight Exposure period: 200h
Test Result(s):
| Evaluated Item | Ref. Standard | Test Condition | Test Result |
| Color difference △E*ab | ASTM D2244-09a | D65 standard light source with 10°observer | 2.2 |
| Grey scale | ISO105-
A02:1993/Cor.2:2005 |
D65 standard light | 3-4 |
| Gloss | ASTM D523-08 | 60o geometry | Gloss before test: 16.3 Gloss after test: 15.1 |
Note: According to ISO105-A02:1993/Cor.2:2005, Grey scale is determined under D65 standard light, grade 5 is the best and grade 1 is the worst.
Reference Sample Test Sample
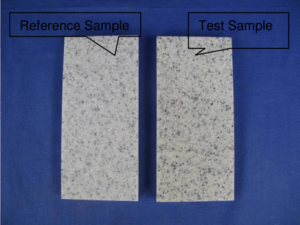
After Xenon-arc Exposure
1.Resistance of Synthetic Polymeric Materials to Fungi Test Method(s):
ASTM G21-1996 (Reapproved 2002) Standard Practice for Determining Resistance of Synthetic Polymeric
Materials to Fungi
Test Organsim(s):
Aspergillus niger ATCC9642, Penicillium pinophilum ATCC11797, Aureobasidium pullulans ATCC15233, Chaetomium globosum ATCC6205, Gliocladium virens ATCC9645
Test result(s):
| Test Culture | Concentration of spores (spores /mL) | Level (after 28 days) |
| Aspergillus niger
ATCC9642 |
1.2×106 |
2 Grade |
| Aureobasidium pullulans ATCC15233 | ||
| Penicillium pinophilum ATCC11797 | ||
| Chaetomium globosum
ATCC6205 |
||
| Gliocladium virens ATCC9645 |
Note: According to ASTM G 21-1996 (Reapproved 2002) Standard Practice for Determining Resistance of Synthetic Polymeric Materials to Fungi, observed fungi growth rating on the specimens include:
- –None
- –Traces of growth (less than 10%) 2 –Light growth (10 to 30%)
- –Medium growth (30 to 60%)
- –Heavy growth (60% to complete coverage)
Fire test Test Requested:
1.To determine the flame spread index (FSI) and smoke-developed index (SDI) of the sample’s surface burning characteristics when it is subjected to the conditions of specified in ASTM E84:2009c “Standard Test Method for Surface Burning Characteristics of Building Materials”
2.To determine the performance of the sample when it is subjected to the conditions of test specified in BS 476 Part 6:1989 + A1:2009 —Fire tests on building materials and structures-Part 6: Method of test for fire propagation for products
3.To determine the performance of the sample when it is subjected to the conditions of test specified in BS 476 Part 7:1997 —Fire tests on building materials and structures Part 7:Method of test to determine the classification of the surface spread of flame products
Sample Details
The details of the tested specimen given below have been prepared from information provided by the sponsor of the test. All values quoted are nominal, unless tolerances are given.
|
General description |
KSTONE Acrylic Solid Surface It is widely
used as all kinds of countertops in commercial and home decoration. |
| Trade Name / Product Reference | Acrylic Solid Surface / KSTONE |
| Name of Manufacturer | SHANGHAI KSTONE INDUSTRIAL CO,.LTD |
|
Composition details |
1). Methyl Methacrylate(MMA):About from 43% to 45%
2). Hydrated Aluminum Oxide Powder(ATH):About 55% 4). Anti-ultraviolet Resin: 0.3% 5). Other:About 2% |
| Color | White color |
| Thickness | 12mm |
| Bulk Density / Mass per unit area | About 1.75g/cm3 |
|
Brief description of manufacturing process |
Our Acrylic Solid Surface product waspolymerized (blended) by Methyl Methacrylate, lsophthalic Resin including anti-UV ultraviolet resin and Hydrated Aluminum Oxide Powder in the vacuum-mixer machine. |
|
End use |
Our Acrylic Solid Surface product was widely used as countertops in public construction such as luxury hotel, laboratory, airport, school, bank and high-class
entertainment place and domestic decoration field. |
Test result:
- ASTM E84:2009c
- Test Conducted
This test was conducted in accordance with ASTM E84:2009c Standard Test Method for Surface Burning Characteristics of Building Materials.
- Introduction
The method, designated as ASTM E 84:09c, “Standard Method of Test for Surface Burning Characteristics of Building Materials”, is designed to determine the relative surface burning characteristics of materials under specific test conditions. Results are expressed in terms of flame spread index (FSI) and smoke developed index (SDI).
The purpose of this test method is to determine the relative burning behavior of the material by observing the flame spread along the specimen. Flame spread and smoke developed index are reported. However, there is not necessarily a relationship between these two measurements.
- Test Procedure
The tunnel is preheated to 150°F, as measured by the floor-embedded thermocouple located 23.25 feet downstream of the burner ports, and allowed to cool to 105°F, as measured by the floor-embedded thermocouple located 13 feet from the burners. At this time the tunnel lid is raised and the test sample is placed along the ledges of the tunnel so as to form a continuous ceiling 24 feet long, 12 inches above the floor. The lid is then lowered into place.
Upon ignition of the gas burners, the flame spread distance is observed and recorded every 15 seconds. Flame spread distance versus time is plotted ignoring any flame front recessions. If the area under the curve (A) is less than or equal to 97.5 min·ft, FSI = 0.515·A; if greater, FSI = 4900/(195-A). Smoke developed is determined by comparing the area under the obscuration curve for the test sample to that of inorganic reinforced cement board and red oak, arbitrarily established as 0 and 100, respectively.
- Conditioning
Prior to testing, the sample was conditioned,
To a constant weight at a temperature of 73.4±5°F (23±2.8°C) and at a relative humidity of 50±5%
Exposed Face:
One face of the specimen was exposed to the flame.
Mounting Methods:
The specimen was self-supporting and was placed directly on the inner ledges of the tunnel.
The specimen consisted of 3 pieces of 2470mm×600mm×12mm scetions jointed end-to-end.
| 5) Test Results | ||
| Sample | FSI | SDI |
| “MODIFIED ACRYLIC SOLID SURFACE” | 5 | 100 |
Rating:
The National Fire Protection Association Life Safety Code 101, Chapter 10, Section 10.2.3 “Interior Wall and Ceiling Finish Classification”, has a means of classifying materials with respect to Flame Spread and Smoke Developed when tested in accordance with NFPA 255, ASTM E84, UL 723 “Method of Test of Surface Burning Characteristics of Building Materials”.
International Building Code, Chapter 8, Interior Finishes, Section 803 “Wall and Ceiling Finishes”, was classified in accordance with ASTM E84 or UL 723. Such interior finish materials shall be grouped in the following classes in accordance with their flame spread and smoke-developed indexes.
| The classifications are as follows: | |||
| Class A | Class B | Class C | |
| Flame Spread Index | 0-25 | 26-75 | 76-200 |
| Smoke-developed Index | 0-450 | 0-450 | 0-450 |
Since the tested sample received a Flame Spread Index 5 and a Smoke Developed 100, it would meet the requirement of Class A interior Wall & Ceiling Finish Category.
OBSERVATIONS
| Time to ignition (sec) | 342 |
| Time to Max. FS (sec) | 469 |
| Maximum FS (feet) | 3 |
NOTE: The use of supporting materials on the underside of the test specimen has the ability to lower the flame spread index from those which might be obtained if the specimen could be tested without such support. These test results do not necessarily relate to indices obtained by testing materials without such support.
Testing of materials that melt, drip, or delaminate to such a degree that the continuity of the flame front is destroyed, results in low flame spread indices that do not relate directly to indices obtained by testing materials that remain in place.
Graphical Results:
- BS 476 Part 6:1989 + A1:2009
- Test conducted
This test was conducted in accordance with the procedure specified in BS 476 Part 6:1989 + A1:2009
—Fire tests on building materials and structures -Part 6: Method of test for fire propagation for products.
- Test details Conditioning:
Prior to testing, the sample was conditioned,
to constant mass at a temperature of 23 ± 2 °C, and a relative humidity of 50 ± 10 %, and maintained in this condition until required for testing.
Exposed Face:
One face of the specimen was exposed to the flame. Form in which the specimens were tested:Material
- Test results
Throughout the test on each specimen, carefully observe the material’s behaviour within the apparatus and take special note of any of the following phenomena listed in clause 9.2 of the standard. None of the listed phenomena was observed and the test results on all three specimens tested were valid.
The index of the performance for the specimen was determined as follows:
S = index of performance for each of the specimens tested and S1, S2 and S3 are sub- indices t = Time in minutes from the origin at which readings are taken
qs = Temperature rise in ℃ for the specimen at time, t
qc = Temperature rise in ℃ for the calibration sheet at time, t
Fire Propagation index
I = i1 + i2 + i3
Where, i1 , i2
and i3 are given by the expressions:
i1 = 13 [(S1 )A + (S1 )B + (S1 )C ], i2 = 13 [(S2 )A + (S2 )B + (S2 )C ], i3 = 13 [(S3 )A + (S3 )B + (S3 )C ]
The following test results were obtained for each specimen tested:
Sub – indices Index of performance
| Specimen No. | ||||
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S | |
| A | 0.68 | 0.63 | 0.49 | 1.79 |
| B | 0.80 | 0.65 | 0.49 | 1.95 |
| C | 0.61 | 0.78 | 0.62 | 2.01 |
Number of Specimens tested
Sub-index i1
Sub-index i2
Sub-index i3
Fire Propagation index I
3 0.70 0.69 0.54 1.92
Note: If a suffix “R” is included in the above fire propagation index I, this indicates that the results should be treated with caution.
- BS 476 Part 7:1997
- Test conducted
This test was conducted in accordance with the procedure specified in BS 476 Part 7:1997 —Fire tests on building materials and structures Part 7. Method of test to determine the classification of the surface spread of flame of products.
- Test details Conditioning:
Prior to testing, the sample was conditioned,
to constant mass at a temperature of 23 ± 2 °C, and a relative humidity of 50 ± 10 %, and maintained in this condition until required for testing.
Exposed Face:
One face of the specimen was exposed to the flame. Specimen mounting:
Each specimen was placed into the specimen holder and backed with a non-combustible insulation board. So that no air gap was provide between the unexposed face of specimen and backing board.
- Test results
| SPECIMEN No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Distance (mm) | Time to travel to indicated distance (minutes :seconds) | |||||
| 75 | 1’11” | 1’10” | 1’10” | 1’09” | 1’09” | 1’11” |
| 165 | 2’07” | 1’51” | 1’49” | 1’54” | 1’54” | 2’04” |
| 190 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 215 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 240 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 265 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 290 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 375 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 455 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 500 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 520 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 600 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 675 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 710 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 750 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 785 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 825 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Maximum distance traveled at 1.5 minutes | 110 | 130 | 135 | 140 | 135 | 115 |
| Maximum distance traveled during the whole test (mm) |
189 |
182 |
185 |
182 |
180 |
185 |
| Time to reach maximum distance traveled | 2’31” | 2’43” | 2’29” | 2’37” | 2’41” | 2’51” |
Note: Six specimens are usually tested. If the test on any specimen is deemed to be invalid, as defined in the standard, it is permissible for up to a maximum of nine specimens to be tested in order to obtain the six valid test results.
The classification limits specified in BS 476-7:1997 are given in Appendix 1. Observations during test:
In the case of specimen No.1, ignited at 57 sec. In the case of specimen No.2, ignited at 54 sec. In the case of specimen No.3, ignited at 54 sec. In the case of specimen No.4, ignited at 51 sec. In the case of specimen No.5, ignited at 53 sec. In the case of specimen No.6, ignited at 57 sec.
Criteria for classification:
If the prefix “D” or suffix “R” or “Y” is included in the classification, this indicates that the results should be treated with caution. An explanation of the reason for prefix and suffixes is given in Appendix 2
Appendix 1 Classification of spread of flame
Spread of flame at 1.5 min Final spread of flame
Classification Limit (mm)
Limit for one specimen in
Limit (mm)
Limit for one specimen in sample(mm)
sample(mm)
| Class 1 | 165 | 165+25 | 165 | 165+25 |
| Class 2 | 215 | 215+25 | 455 | 455+25 |
| Class 3 | 265 | 265+25 | 710 | 710+25 |
Class 4 Exceeding the limits for class 3
Appendix 2 Explanation of prefix and suffixes which may be added to the classification
- A suffix R is added to the classification if more than six specimens are required in order to obtain six valid test results (e.g. class 2R).
- A prefix D is added to the classification of any product which does not conform to the surface characteristics specified in the standard and has therefore been tested in a modified form (e.g. class D3).
- A suffix Y shall be added to the classification if any softening and/or other behaviour that may affect the flame spread occurs
Classification: In accordance with the class definitions given in BS 476 Part 7:1997, the tested samples are classified as class 1.
WARNING:
The test results relate only to the specimens of the product in the form in which were tested. Small differences in the composition or thickness of the product may significantly affect the performance during the test and may therefore invalidate the test results. Care should be taken to ensure that any product, which is supplied or used, is fully represented by the specimens, which were tested.
The specimen was supplied by the sponsor and SGS-CSTC ANJI Branch was not involved in any selection or sampling procedure.
Photo Appendix:

[/fsn_text][/fsn_column][/fsn_row]